Learn More
The Missing Link in Recovery
Recovery is the number one requirement for gains in natural drug free lifters. Without it, results are compromised. Muscle recovery only addresses one half of the equation. Joint recovery is the most overlooked element of intense training and mistakenly taken for granted. MECHAN-X redefines joint recovery and in doing so, will make you rethink the results you may have thought were achievable!
With the 5 best hand-selected joint recovery ingredients, MECHAN-X was created to normalize joint mechanics and restore pain free range of motion throughout your body.
MECHAN-X helps your body in two key ways:
- If you’re constantly shifting the load away from the muscles you’re trying to build to make it easier to handle the joint discomfort you’re feeling, you’ll never get as big or strong as you’d like. Period. By relieving joint pain, MECHAN-X allows you to put the stress of exercise overload back on the muscles it was intended for! No more letting knee pain hold you back from getting bigger legs. No more allowing shoulder pain to keep you from developing the chest and upper body you deserve from your hard training.
- By reducing joint inflammation, MECHAN-X allows you to stop compensating and shifting loads to other joints that are poorly equipped to handle them! Passing the job of the knees onto the low back is the fastest way to injure your lumbar spine! Asking your body to press overhead with poor or altered scapular mechanics is a recipe for chronic shoulder pain! With normalized joint mechanics now in place, you can lift heavier and harder, and recover faster than ever!
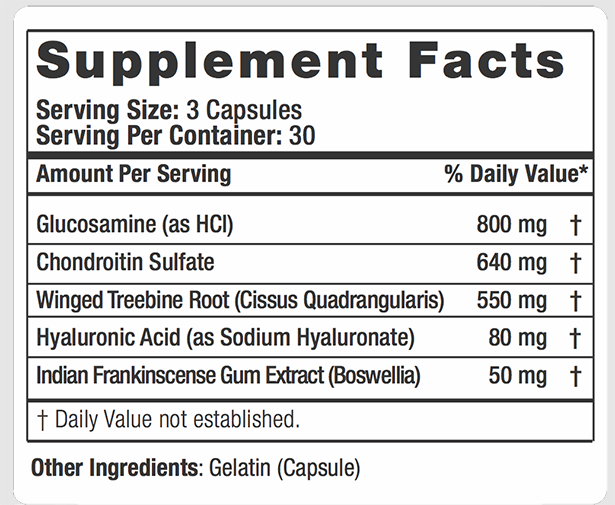
ATHLEAN RX MECHANX
ATHLEAN MECHANX CONTAINS: 800mg
CLINICAL STUDIES
The primary source of nourishment for connective tissue and cartilage. Best dosed in a 5:4 ratio with Chondroitin for maximum absorption and efficacy, as is found in MECHAN-X.
- Faster recovery from injuries
- Pain relief / reduction in pain levels
- Reduction in joint swelling
- Improved physical performance
ATHLEAN MECHANX CONTAINS: 640mg
CLINICAL STUDIES
Used in concert with Glucosamine to restore healthy cartilage to bony surfaces comprising a joint. Best dosed in a 4:5 ratio with Glucosamine for maximum absorption and efficacy, as is found in MECHAN-X.
- Faster recovery from injuries
- Pain relief / reduction in pain levels
- Reduction in joint swelling
- Improved physical performance
ATHLEAN MECHANX CONTAINS: 550mg
CLINICAL STUDIES
Strengthens bones by enhancing calcium uptake. Studies of use in athletes revealed a significant reduction in sidelining bone fractures (6-8 week DL minimum) and speedier recovery from existing breaks.
- Anti-inflammatory agent
- Improves joint pain
- Increases IGF in Bone Cells
- Shown to protect against bone loss
ATHLEAN MECHANX CONTAINS: 80mg
CLINICAL STUDIES
The missing element of a truly complete joint recovery formula, preserving joint fluid viscosity to ensure friction-free joint movement and prevent premature breakdown. When supplemented, has been shown to drastically reduce “warmup time” required to get game ready.
- Supports healthy immune function
- Protects joints from chronic inflammation
ATHLEAN MECHANX CONTAINS: 50mg
CLINICAL STUDIES
The Earth’s natural anti-inflammatory shown to safely and effectively combat joint inflammation at its source and prevent chronic pain from overuse.
- Reduces cartilage degredation
- Reduces pain
- Improves Joint function
REFERENCES
Glucosamine Hydrochloride
-
Bohmer D, Ambrus P, Szogy A, and G. Haralambie. A Treatment of chrondropathia patellae in young athletes with glucosamine sulfate. Current Topics in Sports Medicine, Vienna, Austria: Urban & Schwarzenberg, 1984:799-803.
-
Braham, R. The effect of glucosamine supplementation on people experiencing regular knee pain. Br J Sports Med 2003;37:45-49.
-
Bruyee, O. et al. Correlation between radiographic severity on knee osteoarthritis and future disease progression. Results from a 3-year prospective, placebo-controlled study evaluating the effect of glucosamine sulfate. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2003 jan;11(1):1-5.
-
Burger, Martin et al. Observations of the influence of chondroitin sulphate on the rate of bone repair. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 1962; 44B(3):674-687.
-
Burke E. Nutrients that accelerate healing. Strength and Conditioning 1997:19-23.
-
Crolle, G et al. Glucosamine sulphate for the management of arthrosis: a controlled clinical investigation. Curr. Med Res. Opin 1980; 7(2):104-109.
-
D'Ambrosio E. Glucosamine sulphate: a controlled clinical investigation in arthrosis. Pharmatherapeutica 1981; 2(8):504-508.
-
Das A Jr, Hammad TA. Efficacy of a combination of FCHG49 glucosamine hydrochloride, TRH122 low molecular weight sodium chondroitin sulfate and manganese ascorbate in the management of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2000 Sep;8(5):343-50.
-
Delafuente JC. Glucosamine in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2000;26(1): 1-11.
-
Drovanni A. Therapeutic activity of oral glucosamine sulfate in osteoarthrosis: a placebo-controlled double-blind investigation. Clinical Therapy 1980:260-272.
-
Gottlieb MS. Conservative management of spinal osteoarthritis with glucosamine sulfate and chiropractic treatment. J Manipulative Ther 1997; 20(6):400-414.
-
Kayne SB et al. Is glucosamine an effective treatment for osteoarthritis? A meta-analysis. The Pharmaceutical Journal 2000;265:750-763.
-
Kelly GS. The role of glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin sulfates in the treatment of degenerative joint disease. Altern Med Rev 1998;3(1): 27-39.
-
Leffler CT, Philippi AF, Leffler SG, Mosure JC, Kim PD. Glucosamine, chondroitin, and manganese ascorbate for degenerative joint disease of the knee or low back: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Mil Med. 1999 Feb;164(2):85-91.
-
Lippiello L, Woodward J, Karpman R, Hammad TA. In vivo chondroprotection and metabolic synergy of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate. Clin Orthop. 2000 Dec;(381):229-40.
-
Lippiello L. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate: biological response modifiers of chondrocytes under simulated conditions of joint stress. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003 May;11(5):335-42.
-
Mazieres B et al. Chondroitin sulfate in osteoarthritis of the knee: A prospective, double blind, placebo controlled multicenter clinical study. Journal of Rheumatology 2001;28:173-81.
-
McAlindon TE, MP La Valley, JP Gulin and DT Felson. "Glucosamine and chondroitin for treatment of osteoarthritis: a systematic quality assessment and meta-analysis," JAMA 2000; 283(11):1469-1475.
-
McCarty M. Glucosamine for wound healing. Med Hypotheses 1996;47:273-5.
-
Moss M. The effect of chondroitin sulfate on bone healing. Georgetown University School of Dentistry 1965; 20(6):795-801.
-
Murad H. and Tabibian M. P., The effect of an oral supplement containing glucosamine, amino acids, minerals, and antioxidants on cutaneous aging: a preliminary study. J Dermatolog Treat 2001 Mar;12(1)47-51.
-
Pujalte J et al. Double-blind clinical evaluation of oral glucosamine sulphate in the basic treatment of osteoarthrosis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin 1980; 7(2):110-114.
-
Qiu, G. X., et al. Efficacy and safety of glucosamine sulfate versus ibuprofen in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Arzneimittelforschung 1998 May;48(5):469-474.
-
Reginster J. Effects of glucosamine sulphate on osteoarthritis progression: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Lancet 2001; 357(9252):251-256.
-
Reichelt A, Forster K, Fisher M, et al. Efficacy and safety of intramuscular glucosamine sulfate in osteoarthritis of the knee. A randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Arzneimittelforschung 1994;44:75-80.
-
Rindone J, Hiller D, Collacott E, et al. Randomized, controlled trials of glucosamine for treating osteoarthritis of the knee. West J Med 2000;172:91-4.
-
Ronca, L., et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of chondroitin sulfate. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 1998; 6 Supp:14-21.
-
Setnikar I et al. Antiarthritic effects of glucosamine sulfate studied in animal models, Arzmelm-Forch/Drug Res 1991; 41(5):541-545.
-
Uebelhard, D., et al. Effects of oral chondroitin sulfate on the progression of knee osteoarthritis: a pilot study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1998 May;6 Suppl A:39-46.
-
Vajaradul Y. Double-blind clinical evaluation of intra-articular glucosamine in outpatients with gonarthrosis. Clinical Therapy 1981:336-342.
- van Blitterswijk WJ, van de Nes JC, Wuisman PI. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate supplementation to treat symptomatic disc degeneration: biochemical rationale and case report. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2003 Jun 10;3(1):2.
-
Vaz AL. Double-blind clinical evaluation of the relative efficacy of ibuprofen and glucosamine sulphate in the management of osteoarthrosis of the knee in out-patients. Curr. Med. Res. Opin 1982; 8(3):145-149.
Chondroitin Sulfate
-
Bohmer D, Ambrus P, Szogy A, and G. Haralambie. A Treatment of chrondropathia patellae in young athletes with glucosamine sulfate. Current Topics in Sports Medicine, Vienna, Austria: Urban & Schwarzenberg, 1984:799-803.
-
Braham, R. The effect of glucosamine supplementation on people experiencing regular knee pain. Br J Sports Med 2003;37:45-49.
-
Bruyee, O. et al. Correlation between radiographic severity on knee osteoarthritis and future disease progression. Results from a 3-year prospective, placebo-controlled study evaluating the effect of glucosamine sulfate. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2003 jan;11(1):1-5.
-
Burger, Martin et al. Observations of the influence of chondroitin sulphate on the rate of bone repair. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 1962; 44B(3):674-687.
-
Burke E. Nutrients that accelerate healing. Strength and Conditioning 1997:19-23.
-
Crolle, G et al. Glucosamine sulphate for the management of arthrosis: a controlled clinical investigation. Curr. Med Res. Opin 1980; 7(2):104-109.
-
D'Ambrosio E. Glucosamine sulphate: a controlled clinical investigation in arthrosis. Pharmatherapeutica 1981; 2(8):504-508.
-
Das A Jr, Hammad TA. Efficacy of a combination of FCHG49 glucosamine hydrochloride, TRH122 low molecular weight sodium chondroitin sulfate and manganese ascorbate in the management of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2000 Sep;8(5):343-50.
-
Delafuente JC. Glucosamine in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2000;26(1): 1-11.
-
Drovanni A. Therapeutic activity of oral glucosamine sulfate in osteoarthrosis: a placebo-controlled double-blind investigation. Clinical Therapy 1980:260-272.
-
Gottlieb MS. Conservative management of spinal osteoarthritis with glucosamine sulfate and chiropractic treatment. J Manipulative Ther 1997; 20(6):400-414.
-
Kayne SB et al. Is glucosamine an effective treatment for osteoarthritis? A meta-analysis. The Pharmaceutical Journal 2000;265:750-763.
-
Kelly GS. The role of glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin sulfates in the treatment of degenerative joint disease. Altern Med Rev 1998;3(1): 27-39.
-
Leffler CT, Philippi AF, Leffler SG, Mosure JC, Kim PD. Glucosamine, chondroitin, and manganese ascorbate for degenerative joint disease of the knee or low back: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Mil Med. 1999 Feb;164(2):85-91.
-
Lippiello L, Woodward J, Karpman R, Hammad TA. In vivo chondroprotection and metabolic synergy of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate. Clin Orthop. 2000 Dec;(381):229-40.
-
Lippiello L. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate: biological response modifiers of chondrocytes under simulated conditions of joint stress. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003 May;11(5):335-42.
-
Mazieres B et al. Chondroitin sulfate in osteoarthritis of the knee: A prospective, double blind, placebo controlled multicenter clinical study. Journal of Rheumatology 2001;28:173-81.
-
McAlindon TE, MP La Valley, JP Gulin and DT Felson. "Glucosamine and chondroitin for treatment of osteoarthritis: a systematic quality assessment and meta-analysis," JAMA 2000; 283(11):1469-1475.
-
McCarty M. Glucosamine for wound healing. Med Hypotheses 1996;47:273-5.
-
Moss M. The effect of chondroitin sulfate on bone healing. Georgetown University School of Dentistry 1965; 20(6):795-801.
-
Murad H. and Tabibian M. P., The effect of an oral supplement containing glucosamine, amino acids, minerals, and antioxidants on cutaneous aging: a preliminary study. J Dermatolog Treat 2001 Mar;12(1)47-51.
-
Pujalte J et al. Double-blind clinical evaluation of oral glucosamine sulphate in the basic treatment of osteoarthrosis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin 1980; 7(2):110-114.
-
Qiu, G. X., et al. Efficacy and safety of glucosamine sulfate versus ibuprofen in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Arzneimittelforschung 1998 May;48(5):469-474.
-
Reginster J. Effects of glucosamine sulphate on osteoarthritis progression: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Lancet 2001; 357(9252):251-256.
-
Reichelt A, Forster K, Fisher M, et al. Efficacy and safety of intramuscular glucosamine sulfate in osteoarthritis of the knee. A randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Arzneimittelforschung 1994;44:75-80.
-
Rindone J, Hiller D, Collacott E, et al. Randomized, controlled trials of glucosamine for treating osteoarthritis of the knee. West J Med 2000;172:91-4.
-
Ronca, L., et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of chondroitin sulfate. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 1998; 6 Supp:14-21.
-
Setnikar I et al. Antiarthritic effects of glucosamine sulfate studied in animal models, Arzmelm-Forch/Drug Res 1991; 41(5):541-545.
-
Uebelhard, D., et al. Effects of oral chondroitin sulfate on the progression of knee osteoarthritis: a pilot study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1998 May;6 Suppl A:39-46.
-
Vajaradul Y. Double-blind clinical evaluation of intra-articular glucosamine in outpatients with gonarthrosis. Clinical Therapy 1981:336-342.
- van Blitterswijk WJ, van de Nes JC, Wuisman PI. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate supplementation to treat symptomatic disc degeneration: biochemical rationale and case report. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2003 Jun 10;3(1):2.
-
Vaz AL. Double-blind clinical evaluation of the relative efficacy of ibuprofen and glucosamine sulphate in the management of osteoarthrosis of the knee in out-patients. Curr. Med. Res. Opin 1982; 8(3):145-149.
Cissus Quandrangularis
-
Bah, S., Paulsen, B. S., Diallo, D., and Johansen, H. T. Characterization of cysteine proteases in Malian medicinal plants. J Ethnopharmacol. 9-19-2006;107(2):189-198. View abstract.
-
Balachandran, B., Sivaswamy, S. N., and Sivaramakrishnan, V. M. Genotoxic effects of some foods & food components in Swiss mice. Indian J Med Res 1991;94:378-383. View abstract.
-
Bhujade, A. M., Talmale, S., Kumar, N., Gupta, G., Reddanna, P., Das, S. K., and Patil, M. B. Evaluation of Cissus quadrangularis extracts as an inhibitor of COX, 5-LOX, and proinflammatory mediators. J Ethnopharmacol. 6-14-2012;141(3):989-996. View abstract.
-
Bongaard, BS. Botanical Agents for the Treatment of Obesity, Lipid Abnormalities, and Metabolic Syndrome. Alternative Medicine Alert 2007;10(8):85-88.
-
Chidambara Murthy, K. N., Vanitha, A., Mahadeva, Swamy M., and Ravishankar, G. A. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of Cissus quadrangularis L. J Med Food 2003;6(2):99-105. View abstract.
-
Chidambaram, J. and Carani, Venkatraman A. Cissus quadrangularis stem alleviates insulin resistance, oxidative injury and fatty liver disease in rats fed high fat plus fructose diet. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48(8-9):2021-2029. View abstract.
-
Chopra, S. S., Patel, M. R., and Awadhiya, R. P. Studies of Cissus quadrangularis in experimental fracture repair : a histopathological study. Indian J Med Res 1976;64(9):1365-1368. View abstract.
-
Chopra, S. S., Patel, M. R., Gupta, L. P., and Datta, I. C. Studies on Cissus quadrangularis in experimental fracture repair: effect on chemical parameters in blood. Indian J Med Res 1975;63(6):824-828. View abstract.
-
Das PK, Sanyal AK. Studies on Cissus Quadrangularis Linn. I. Acetylcholine Like Action of the Total Extract. Indian J Med Res 1964;52:63-67. View abstract.
-
de Almeida ER, de Oliveira JR Lucena FF Soares RP Couto GB. The action of extract of the dry leaves of Cissus sicyoides L. in pregnant rats. Acta Farmaceutica Bonaerense (Argentina) 2006;25:421-424.
-
Dhatrak Sarang, Thawani Vijay Gharpure Kunda Apte Indrayani Masand Anil Hingorani Lal and Khiyani Raj. Effect of Herbal Combination in Low Bone Mass Density Patients. International Journal of Drug Discovery and Technology 2011;2(1):9-14.
-
Hasani-Ranjbar, S., Nayebi, N., Larijani, B., and Abdollahi, M. A systematic review of the efficacy and safety of herbal medicines used in the treatment of obesity. World J Gastroenterol. 7-7-2009;15(25):3073-3085. View abstract.
-
Hema R, Kumaravel S Ruffina D. Antimicrobial activity of some Indian herbs against plant pathogens. Australian Journal of Medical Herbalism 2010;22(4):138-139.
-
Jain, A., Dixit, J., and Prakash, D. Modulatory effects of Cissus quadrangularis on periodontal regeneration by bovine-derived hydroxyapatite in intrabony defects: exploratory clinical trial. J Int.Acad.Periodontol. 2008;10(2):59-65. View abstract.
-
Jainu M, Shyamala Devi CS. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Free-Radical Scavenging Potential of Cissus quadrangularis. Pharmaceutical Biology 2005;43(9):773-779.
-
Jainu, M. and Devi, C. S. Effect of Cissus quadrangularis on gastric mucosal defensive factors in experimentally induced gastric ulcer-a comparative study with sucralfate. J Med Food 2004;7(3):372-376. View abstract.
-
Jainu, M. and Mohan, K. V. Protective role of ascorbic acid isolated from Cissus quadrangularis on NSAID induced toxicity through immunomodulating response and growth factors expression. Int.Immunopharmacol. 12-20-2008;8(13-14):1721-1727. View abstract.
-
Jainu, M. and Shyamala Devi, C. S. Attenuation of neutrophil infiltration and proinflammatory cytokines by Cissus quadrangularis: a possible prevention against gastric ulcerogenesis. J Herb.Pharmacother. 2005;5(3):33-42. View abstract.
-
Jainu, M., Mohan, K. V., and Devi, C. S. Protective effect of Cissus quadrangularis on neutrophil mediated tissue injury induced by aspirin in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 4-6-2006;104(3):302-305. View abstract.
-
Jainu, M., Vijaimohan, K., and Kannan, K. Cissus quadrangularis L. extract attenuates chronic ulcer by possible involvement of polyamines and proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Pharmacogn.Mag. 2010;6(23):225-233. View abstract.
-
Kumar, M., Rawat, P., Dixit, P., Mishra, D., Gautam, A. K., Pandey, R., Singh, D., Chattopadhyay, N., and Maurya, R. Anti-osteoporotic constituents from Indian medicinal plants. Phytomedicine 2010;17(13):993-999. View abstract.
-
Kumar, R., Sharma, A. K., Saraf, S. A., and Gupta, R. CNS activity of aqueous extract of root of cissus quadrangularis linn. (Vitaceae). J Diet.Suppl 2010;7(1):1-8. View abstract.
-
Mehta, M., Kaur, N., and Bhutani, K. K. Determination of marker constituents from Cissus quadrangularis Linn. and their quantitation by HPTLC and HPLC. Phytochem.Anal. 2001;12(2):91-95. View abstract.
-
Muthusami, S., Senthilkumar, K., Vignesh, C., Ilangovan, R., Stanley, J., Selvamurugan, N., and Srinivasan, N. Effects of Cissus quadrangularis on the proliferation, differentiation and matrix mineralization of human osteoblast like SaOS-2 cells. J Cell Biochem 2011;112(4):1035-1045. View abstract.
-
O'Mathúna DP. Herbal Remedies for Weight Loss. Alternative Medicine Alert 2011;14(4):37.
-
Opoku, A. R., Geheeb-Keller, M., Lin, J., Terblanche, S. E., Hutchings, A., Chuturgoon, A., and Pillay, D. Preliminary screening of some traditional Zulu medicinal plants for antineoplastic activities versus the HepG2 cell line. Phytother.Res 2000;14(7):534-537. View abstract.
-
Panpimanmas, S., Sithipongsri, S., Sukdanon, C., and Manmee, C. Experimental comparative study of the efficacy and side effects of Cissus quadrangularis L. (Vitaceae) to Daflon (Servier) and placebo in the treatment of acute hemorrhoids. J Med Assoc.Thai. 2010;93(12):1360-1367. View abstract.
-
Parisuthiman, D., Singhatanadgit, W., Dechatiwongse, T., and Koontongkaew, S. Cissus quadrangularis extract enhances biomineralization through up-regulation of MAPK-dependent alkaline phosphatase activity in osteoblasts. In Vitro Cell Dev.Biol.Anim 2009;45(3-4):194-200. View abstract.
-
Potu, B. K., Bhat, K. M., Rao, M. S., Nampurath, G. K., Chamallamudi, M. R., Nayak, S. R., and Muttigi, M. S. Petroleum ether extract of Cissus quadrangularis (Linn.) enhances bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and facilitates osteoblastogenesis. Clinics.(Sao Paulo) 2009;64(10):993-998. View abstract.
-
Potu, B. K., Nampurath, G. K., Rao, M. S., and Bhat, K. M. Effect of Cissus quadrangularis Linn on the development of osteopenia induced by ovariectomy in rats. Clin Ter. 2011;162(4):307-312. View abstract.
-
Potu, B. K., Rao, M. S., Kutty, N. G., Bhat, K. M., Chamallamudi, M. R., and Nayak, S. R. Petroleum ether extract of Cissus quadrangularis (LINN) stimulates the growth of fetal bone during intra uterine developmental period: a morphometric analysis. Clinics.(Sao Paulo) 2008;63(6):815-820. View abstract.
-
Potu, B. K., Rao, M. S., Nampurath, G. K., Chamallamudi, M. R., Nayak, S. R., and Thomas, H. Anti-osteoporotic activity of the petroleum ether extract of Cissus quadrangularis Linn. in ovariectomized Wistar rats. Chang Gung.Med J 2010;33(3):252-257. View abstract.
-
Potu, B. K., Rao, M. S., Nampurath, G. K., Chamallamudi, M. R., Prasad, K., Nayak, S. R., Dharmavarapu, P. K., Kedage, V., and Bhat, K. M. Evidence-based assessment of antiosteoporotic activity of petroleum-ether extract of Cissus quadrangularis Linn. on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis. Ups.J Med Sci 2009;114(3):140-148. View abstract.
-
PRASAD, G. C. and UDUPA, K. N. EFFECT OF CISSUS QUADRANGULARIS ON THE HEALING OF CORTISONE TREATED FRACTURES. Indian J Med Res 1963;51:667-676. View abstract.
-
Shah, U. M., Patel, S. M., Patel, P. H., Hingorani, L., and Jadhav, R. B. Development and Validation of a Simple Isocratic HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Phytosterols in Cissus quadrangularis. Indian J Pharm.Sci 2010;72(6):753-758. View abstract.
-
Shanthi G, Vijay kanth G Hitesh L Ganesan M. Antiulcerogenic activities of the methanolic extract of Cissus quadrangularis in wistar. Internet Journal of Toxicology 2010;7(2)
-
Shirwaikar, A., Khan, S., and Malini, S. Antiosteoporotic effect of ethanol extract of Cissus quadrangularis Linn. on ovariectomized rat. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003;89(2-3):245-250. View abstract.
-
Singh SP, Misra N Dixit KS et al. An experimental study of analgesic activity of cissus quadrangularis. Indian Journal of Pharmacology 1984;16(3):162-163.
-
SINGH, L. M. and UDUPA, K. N. Studies on "Cissus Quadrangularis" in fracture by using phosphorus 32. III. Indian J Med Sci 1962;16:926-931. View abstract.
-
Sivaswamy, S. N., Balachandran, B., Balanehru, S., and Sivaramakrishnan, V. M. Mutagenic activity of south Indian food items. Indian J Exp.Biol. 1991;29(8):730-737. View abstract.
-
Srisook, K., Palachot, M., Mongkol, N., Srisook, E., and Sarapusit, S. Anti-inflammatory effect of ethyl acetate extract from Cissus quadrangularis Linn may be involved with induction of heme oxygenase-1 and suppression of NF-kappaB activation. J Ethnopharmacol. 2-16-2011;133(3):1008-1014. View abstract.
-
Thawani VR, Kimmatkar N Hingorani LL Khiyani RM. Effect of herbal combination containing cissus quadrangularis in fracture healing. The Antiseptic 2002;99(9):345-347.
-
UDUPA, K. N. and PRASAD, G. BIOMECHANICAL AND CALCIUM-45 STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF CISSUS QUADRANGULARIS IN FRACTURE REPAIR. Indian J Med Res 1964;52:480-487. View abstract.
-
UDUPA, K. N. and PRASAD, G. C. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF CISSUS QUADRANGULARIS IN ACCELERATING FRACTURE HEALING. Indian J Med Res 1964;52:26-35. View abstract.
-
UDUPA, K. N., ARNIKAR, H. J., and SINGH, L. M. Experimental studies of the use of 'cissus quadrangularis' in healing of fractures. II. Indian J Med Sci 1961;15:551-557. View abstract.
-
Viswanatha Swamy, A. H., Kulkarni, R. V., Thippeswamy, A. H., Koti, B. C., and Gore, A. Evaluation of hepatoprotective activity of Cissus quadrangularis stem extract against isoniazid-induced liver damage in rats. Indian J Pharmacol. 2010;42(6):397-400. View abstract.
-
Bah S, Jager AK, Adsersen A, et al. Antiplasmodial and GABA(A)-benzodiazepine receptor binding activities of five plants used in traditional medicine in Mali, West Africa. J Ethnopharmacol 2007;110:451-7. View abstract.
-
Barakat SEM, Adam SEI, Maglad MA, Wasfi IA. Effects of Cissus quadrangularis on goats and sheep in Sudan. Rev Elev Med Vet Pays Trop 1985;38:185-94. View abstract.
-
Jainu M, Devi CS. Gastroprotective action of Cissus quadrangularis extract against NSAID induced gastric ulcer: role of proinflammatory cytokines and oxidative damage. Chem Biol Interact 2006;161:262-70. View abstract.
-
Jainu M, Mohan KV, Devi CSS. Gastroprotective effect of Cissus quadrangularis extract in rats with experimentally induced ulcer. Indian J Med Res 2006;123:799-806. View abstract.
-
Oben J, Enyegue DM, Fomekong G, et al. The effect of Cissus quadrangularis (CQR-300) and a Cissus formulation (CORE) on obesity and obesity-induced oxidative stress. Lipids Health Dis 2007;6:4. View abstract.
-
Oben J, Kuate D, Agbor G, et al. The use of a Cissus quadrangularis formulation in the management of weight loss and metabolic syndrome. Lipids Health Dis 2006, 5:24. View abstract.
-
Oben JE, Ngondi JL, Momo CN, et al. The use of Cissus quadrangularis/Irvingia gabonensis combination in the management of weight loss: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Lipids Health Dis 2008;7:12. View abstract.
-
Panthong A, Supraditaporn W, Kanjanapothi D, et al. Analgesic, anti-inflammatory and venotonic effects of Cissus quadrangularis Linn. J Ethnopharmacol 2007;110:264-70. View abstract.
-
Singh G, Rawat P, Maurya R. Constituents of Cissus quadrangularis. Nat Prod Res 2007;21:522-8. View abstract.
Hyaluronic Acid
- Iwaso H, Sato T. Examination of the efficacy and safety of oral administration of Hyabest J, highly pure hyaluronic acid, for knee joint pain. Journal of Japanese Society of Clinical Sports Medicine. 2009;17(3):566–572.
- ScientificWorldJournal. 2012; 2012: 167928.
Published online 2012 Nov 20. doi: 10.1100/2012/167928
PMCID: PMC3512263
Oral Administration of Polymer Hyaluronic Acid Alleviates Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study over a 12-Month Period
Toshiyuki Tashiro, 1 Satoshi Seino, 2 Toshihide Sato, 2 Ryosuke Matsuoka, 2 ,* Yasunobu Masuda, 2 and Naoshi Fukui 3 - Nagaoka I, Nabeshima K, Murakami S, et al. Evaluation of the effects of a supplementary diet containing chicken comb extract on symptoms and cartilage metabolism in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2010;1(5):817–827. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kalman DS, Heimer M, Valdeon A, Schwartz H, Sheldon E. Effect of a natural extract of chicken combs with a high content of hyaluronic acid (Hyal-Joint) on pain relief and quality of life in subjects with knee osteoarthritis: a pilot randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Nutrition Journal. 2008;7(1, article 3) [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Boswellia Serrata
- Sengupta K, et al Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 5-Loxin and AflapinAgainst osteoarthritis of the knee: a double blind, randomized, placebo controlled clinical study. Int J Med Sci. (2010)
- Gupta PK, et al Clinical evaluation of Boswellia serrata (Shallaki) resin in the management of Sandhivata (osteoarthritis) .Ayu. (2011)
- Vishal AA, Mishra A, Raychaudhuri SP A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled clinical study evaluates the early efficacy of aflapin in subjects with osteoarthritis of knee. Int J Med Sci. (2011)
- Gupta I, et alEffects of Boswellia serrata gum resin in patients with bronchial asthma: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, 6-week clinical study . Eur J Med Res. (1998)
- Pedretti A, et al Effects of topical boswellic acid on photo and age-damaged skin: clinical, biophysical, and echographic evaluations in a double-blind, randomized, split-face study . Planta Med. (2010)
- Sengupta K, et alA double blind, randomized, placebo controlled study of the efficacy and safety of 5-Loxin for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Res Ther. (2008)
- Flavin DF A lipoxygenase inhibitor in breast cancer brain metastases. J Neurooncol. (2007)